Basic Knowledge of Tact Switch
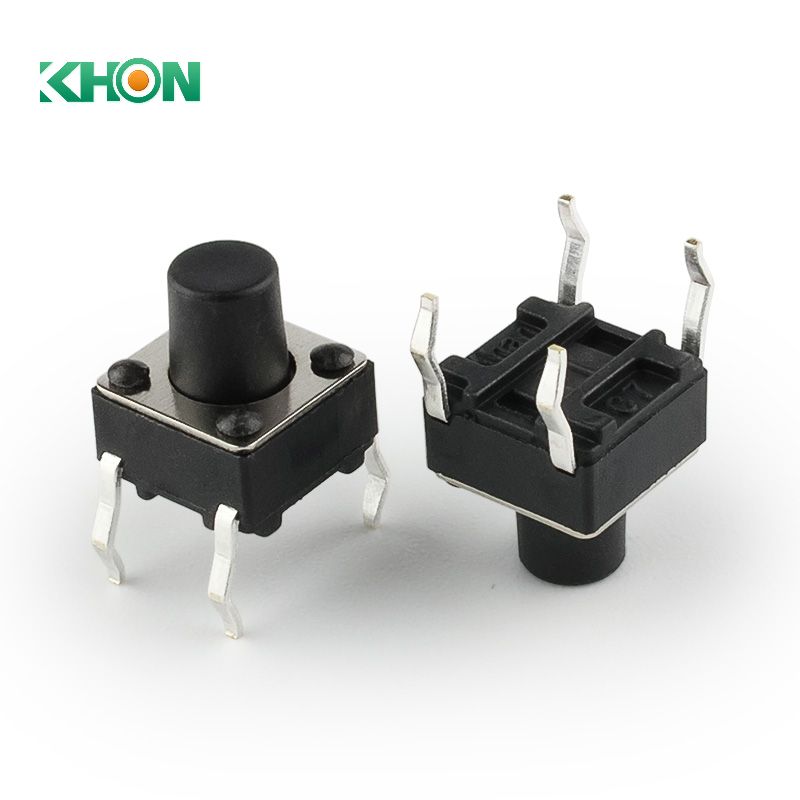


⒈ What is a Tact Switch?
A tact switch, as a highly prevalent type of switch, fundamentally operates by establishing electrical connections when the user applies slight pressure. It provides users with a distinct tactile or audible "click" feedback, confirming the successful flow of current. Once released, the flow of current ceases. In essence, a tact switch is a device that offers instant responsiveness through tactile sensation, ensuring users have a clear perception of switch operation and signal flow. Additionally, there is a special type of tact switch known as a "normally closed" tact switch, which interrupts the current when pressed and restores the connection when released, offering users a more diverse range of options.
⒉ Differences Between Tact Switches and Push Button Switches
Users might mistakenly refer to tact switches as push button switches. Push button switches allow current to flow through the circuit when pressed and stop the flow when pressed again. In contrast, tact switches allow current to flow when pressed and held, and stop the flow when released, or vice versa. They are referred to as "momentary action" switches. Tact switches are typically much smaller than push button switches, due to their design, usually carry lower voltage and current ratings.
⒊ Characteristics and Advantages of Tact Switches
Instantaneous Circuit Connection: Tact switches allow current to flow when pressed and break the circuit when released, or vice versa. This design supports rapid data input, such as on computer keyboards, or continuous operation when needed, such as motor control keyboards.
Tactile and Audible Feedback: Tact switches provide clear feedback to operators, confirming that the switch is engaged and power is flowing to the circuit. In applications like computer keyboards, they also offer satisfying physical "feel," aiding in indicating missed hits or insufficient input.
Low Power and Current Operation: Tact switches typically operate at lower power and current levels, reducing production costs and making them suitable for low-voltage devices and systems. Lower voltage also reduces arcing at the contact points.
Long Lifespan: Tact switches, due to their fewer moving parts, generally have a longer lifespan than other mechanical switches. They can be directly mounted onto circuit boards, reducing the need for maintenance. Their usage cost in products is lower compared to other types of switches.
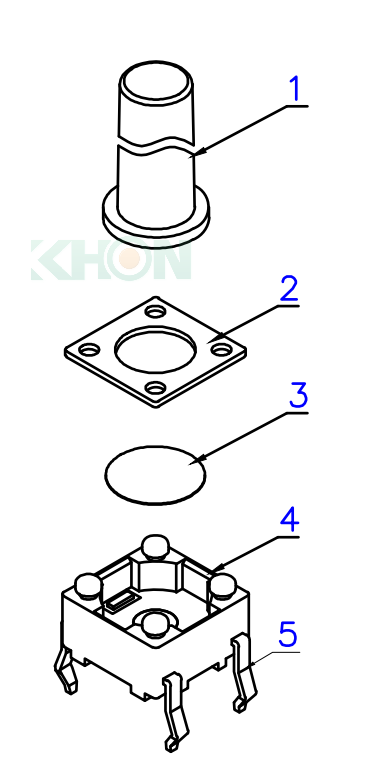
⒋ Basic Structure and Operation of a Tact Switch
1. Stem
2. Cover
3. Contact
4. Holder
5. Terminal
⒌ Specifications of Tact Switches:
Choosing the right tact switch entails more than just evaluating the specifications listed on the product datasheet. Tact switches, due to their "feel" and "sound," can influence users' perception of the overall product quality. This perception may be challenging to quantify.
Nevertheless, tact switches have several design specifications applicable, including:
1. Voltage Rating: (sometimes referred to as rated power) indicates the maximum voltage the switch can withstand when open or closed. Touch switches typically have lower voltage ratings.
2. Current Rating: maximum current the switch can handle before damage occurs (expressed in amperes).
3. Actuation Force: (also known as operating force) the force or pressure required to actuate the actuator on the switch (expressed in grams-force or gf).
4. Travel: the total distance traveled when pressing the switch.
5. Height: the height of the switch body.
6. Lifespan: the expected number of cycles the switch can endure under normal operating conditions.
7. Temperature Range: the temperature range within which the switch operates according to specifications.
8. Mounting Method: how the switch is mounted on the PCB, which can be through-hole or surface mount.
9. IP Rating: an international standard that classifies the protection level against dust and water ingress for switches (or other products).
⒍ Types of Tact Switches:
Tact switches come in two main types: standard (or open) and sealed. Standard tact switches lack sealing against external elements such as dust, gases, or water. Sealed touch switches, on the other hand, feature mechanical components to protect internal parts from dust and water ingress in harsh environments.
Different types of touch switches include:
- Circular/Square/Rectangular
- Flat type
- Illuminated
- Micro
- Miniature
- Right-angle
- Long-travel
- Tactile
- Switch arrays and keyboards
⒎ Wiring Tact Switches:
Tact switches typically come with 4 pins, which are internally connected into 2 sets. The purpose of using 4 pins is to provide stability when the device is mounted on a circuit board. There are also versions of tact switches with only 2 pins. Additionally, there are tact switches with 5 pins, used to provide joystick-like control in very small packages.
⒏ Applications of Tact Switches:
Due to their small size, low profile, and long lifespan, tact switches are suitable for various needs in consumer and industrial products.
Consumer Electronics: Including smartphones, remote controls, portable music players, and cameras.
Medical Devices: Tact switches are crucial for reliable operation in applications such as glucometers and other portable monitoring devices.
Industrial Control: In control panels and industrial equipment, tact switches are used for input devices and limit switches.
Computer Hardware: Tact switches are commonly used in computer peripherals such as keyboards and mice.
Home Appliances: Tact switches are commonly found on control panels for microwaves, televisions, and other home appliances.
Automotive: Inside automobiles, tact switches are used to control lighting, audio systems, and other functions.
Virtual Reality: In VR controllers and other gaming devices, tact switches provide rapid response and haptic feedback.
⒐ Conclusion:
In product design, when low-power, momentary-action power control, or data input becomes a necessary element, tact switches are undoubtedly a wise choice. Especially when tactile and auditory feedback are needed to enhance the user experience, the characteristics of touch switches make them an ideal choice.
■


